




Gurobi allows energy and utility companies to respond to the growing demand for services each year. Optimization enables organizations to delicately balance consumer utilization with responsible management of power generation and distribution. Optimization allows companies to turn data into insight by combining economic, social, and environmental considerations into a single mathematical model. Optimization can also be used to help companies mitigate risk and uncertainty in an increasingly competitive market.
Gurobi delivers blazing speeds and advanced features—backed by brilliant innovators and expert support.
Gurobi’s powerful MIP algorithm allows you to add complexity to your model to better represent the real world, and still solve your model within the available time.
Our development team includes the brightest minds in decision-intelligence technology--and they're continually raising the bar in terms of solver speed and functionality.
Our PhD-level experts are here when you need them—ready to provide comprehensive guidance and technical support. They bring deep expertise in working with commercial models and are there to assist you throughout the process of implementing and using Gurobi.

Dive deep into sample models, built with our Python API.
Facility location problems can be commonly found in many industries, including logistics and telecommunications. In this example, we’ll show you how to tackle a facility location problem that involves determining the number and location of warehouses that are needed to supply a group of supermarkets. We’ll demonstrate how to construct a mixed-integer programming (MIP) model of this problem, implement this model in the Gurobi Python API, and then use the Gurobi Optimizer to find an optimal solution. This modeling example is at the beginner level, where we assume that you know Python and that you have some knowledge about building mathematical optimization models.
Learn MoreIn this example, you’ll learn how to solve an offshore wind power generation problem. The goal of the problem is to figure out which underwater cables should be laid to connect an offshore wind farm power network at a minimum cost. We’ll show you how to formulate a mixed-integer programming (MIP) model of this problem using the Gurobi Python API and then find an optimal solution to the problem using the Gurobi Optimizer. This modeling example is at the beginner level, where we assume that you know Python and that you have some knowledge about building mathematical optimization models.
Learn MoreTry this modeling example to discover how mathematical optimization can help telecommunications firms automate and improve their technician assignment, scheduling, and routing decisions in order to ensure the highest levels of customer satisfaction. This modeling example is at the intermediate level, where we assume that you know Python and are familiar with the Gurobi Python API. In addition, you have some knowledge about building mathematical optimization models. To fully understand the content of this notebook, you should be familiar with object-oriented-programming.
Learn More
Prescriptive analytics tools like Gurobi equip you to make optimal business decisions in the midst of extreme complexity. For example, you can decide exactly which products to produce, in which quantities, in which order, and in which facilities, while taking into consideration production minimums, manufacturing time and costs, raw material inventory, and inventory capacity, in order to minimize total product costs.
Prescriptive analytics is one of the three main types of data analytics, as show below:
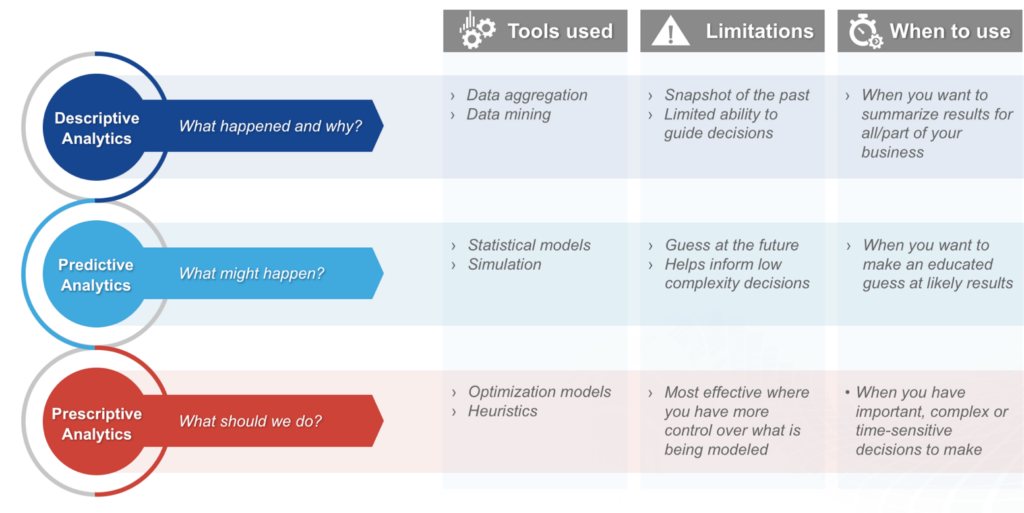
Predictive analytics tools—like machine learning, statistical models, and simulations—seek to find patterns in data, in order to predict what might happen in the future. For example, you can estimate industry growth, raw material pricing, revenue or profit growth, or changes in demand by product line.
Predictive analytics looks for patterns in historical data and uses those patterns to make predictions about the future. Prescriptive analytics can help you find the optimal way to achieve your business goals, given those predictions.
For example, if you were planning a trip, machine learning can predict what you may encounter along your journey (weather, traffic, engine trouble). But with mathematical optimization, you can take those predictions into consideration, as well as your goals (fastest, cheapest, safest route) and constraints (time, budget, speed limits), and identify the single best road you should take.
One popular prescriptive analytics use case is marketing campaign optimization—enabling you to offer the right product to the right person at the right time, so you can maximize your marketing ROI while satisfying your business constraints.
Another example is production planning:
Your goals/objectives:
Your constraints:
Your decision variables (the questions you need answered):
Other examples include inventory optimization, location planning, portfolio management, vehicle routing, workforce scheduling, and more.
No results found.
We make it easy for students, faculty, and researchers to work with mathematical optimization.
When you face complex optimization challenges, you can trust our Gurobi Alliance partners for expert services.
Our global team of helpful, PhD-level experts are here to support you—with responses in hours, not days.
GUROBI NEWSLETTER
Latest news and releases
Privacy Policy | © Gurobi Optimization, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |